The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, relying on an intricate, invisible communication network to maintain homeostasis and regulate nearly every physiological process. At the core of this vast regulatory network lies the field of medical science dedicated to chemical messengers: endocrinology. This specialized branch of internal medicine focuses on the study of hormones, the endocrine glands that secrete them, and the complex metabolic pathways they govern. When this delicate chemical balance is disrupted, it can precipitate widespread systemic effects. For patients seeking comprehensive, advanced care to manage these biochemical imbalances, specialized medical institutions likeLiv Hospital offer the multidisciplinary expertise required to restore optimal health.
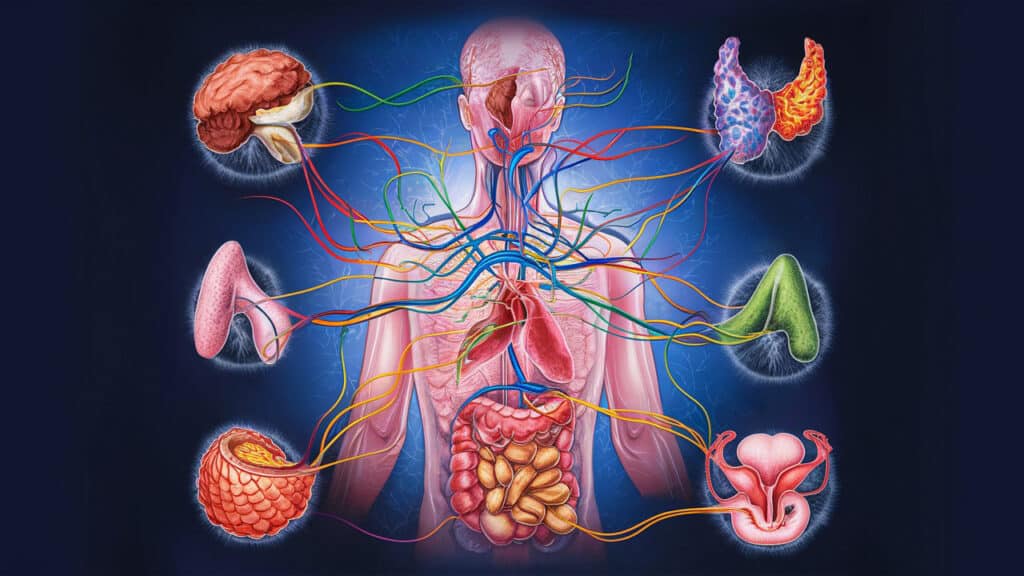
The Architecture of the Endocrine System
Unlike the nervous system, which uses electrical impulses for rapid, short-acting communication, the endocrine system utilizes hormones—chemical messengers secreted directly into the bloodstream. These hormones travel throughout the body, binding to specific cellular receptors to initiate prolonged, sustained changes in target tissues. The system operates on highly sensitive feedback loops, constantly monitoring blood concentrations of various substances to increase or decrease hormone production as needed.
Several primary glands comprise this vital network, each with distinct physiological responsibilities:
- The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: Often referred to as the “command center,” these structures located in the brain dictate the function of most other endocrine glands. The pituitary secretes stimulating hormones that regulate growth, reproduction, and metabolic rate.
- The Thyroid Gland: Situated in the anterior neck, this butterfly-shaped gland produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are the primary drivers of basal metabolic rate, influencing how the body utilizes energy, regulates internal temperature, and supports cardiac function.
- The Pancreas: Functioning as both an exocrine and an endocrine organ, the pancreas contains clusters of cells known as the Islets of Langerhans. These cells secrete insulin and glucagon, the master hormones responsible for maintaining precise blood glucose levels.
- The Adrenal Glands: Located atop the kidneys, these glands produce cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenaline. They are essential for managing the body’s response to acute and chronic stress, regulating blood pressure, and balancing essential electrolytes.
Prevalent Endocrine Pathologies
Because hormones influence virtually every cell, organ, and function of the human body, endocrine disorders manifest in highly diverse ways. Some conditions arise from the overproduction of a hormone (hypersecretion), while others stem from an insufficient supply (hyposecretion) or an inability of the body’s tissues to respond appropriately to the chemical signal. Medical professionals specializing inENDOCRINOLOGY are tasked with diagnosing and managing these often-chronic conditions.
Diabetes Mellitus remains the most globally prevalent endocrine disorder. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system erroneously destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas, necessitating lifelong exogenous insulin therapy. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for the vast majority of cases, is primarily characterized by insulin resistance; the body produces insulin, but cellular receptors fail to respond effectively, leading to elevated blood sugar levels that can damage the vasculature, kidneys, and nervous system over time.
Thyroid Disorders are equally widespread. Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid), often caused by the autoimmune condition Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, leads to pervasive fatigue, unexplained weight gain, and cognitive slowing. Conversely, hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid), frequently linked to Graves’ disease, accelerates the metabolism, causing rapid heart rate, severe weight loss, and debilitating anxiety.
Modern Diagnostics and Clinical Interventions
The diagnostic process in endocrinology is highly analytical, relying heavily on sophisticated laboratory assays. Clinicians measure specific hormone levels in the blood, urine, or saliva. Because hormone secretion often fluctuates throughout the day according to circadian rhythms, dynamic testing is frequently employed. This involves administering a stimulating or suppressing agent and measuring the body’s hormonal response over several hours to pinpoint the exact location of a dysfunction along the endocrine axis. Advanced imaging modalities, such as high-resolution ultrasound, MRI, and specialized nuclear medicine scans, are also utilized to identify structural abnormalities like benign adenomas or malignant tumors on the glands.
Once an accurate diagnosis is established, treatment protocols are meticulously tailored. Endocrine therapy often involves hormone replacement for hyposecretion disorders, such as prescribing synthetic levothyroxine for a failing thyroid. For hypersecretion, physicians may utilize medications that block the synthesis of the offending hormone, or recommend surgical resection or targeted radiation to reduce the glandular tissue.
Sustaining Hormonal Harmony
While clinical interventions and pharmacological therapies are paramount for treating diagnosed endocrine diseases, the foundational role of daily lifestyle factors cannot be overstated. The endocrine system is exquisitely sensitive to external inputs, meaning that environmental stressors, nutritional deficiencies, and sleep architecture profoundly impact hormonal balance. Chronic psychological stress, for example, maintains elevated cortisol levels, which can subsequently induce insulin resistance and disrupt reproductive hormones. Modulating these physiological responses requires a dedicated approach to restorative sleep, balanced macronutrient intake to stabilize blood glucose, and proactive stress mitigation. For individuals looking to explore how these foundational daily choices shape systemic wellness and to discover actionable strategies for supporting physiological equilibrium, resources likelive and feel offer expert guidance on nurturing long-term vitality.